PRP can help tighten the skin, reduce lines and wrinkles, reduce puffiness and dark circles under the eyes, improve overall skin quality, improve skin elasticity after cosmetic surgery, make a dull complexion look better, boost the benefits of nonsurgical rejuvenation.
How Is The Procedure Done?
The PRP treatment is quick and very well tolerated by the majority of patients. Your skin is cleansed and prepared while the platelets are collected. The PRP is then injected into the problem areas in a 15-minute procedure.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is made from two parts: plasma, the liquid part of blood, and platelets, blood cells that help heal the body. Platelets are known for clotting, but they also have growth factors that promote cell growth and tissue healing. To make PRP, we take a blood sample from the patient and spin it in a centrifuge to separate and concentrate the platelets.
About Platelet-rich plasma
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a medical treatment that uses a patient’s own blood to promote healing and regeneration in various tissues. It is widely used in dermatology, orthopedics, and sports medicine, and has gained popularity for its potential benefits in skin rejuvenation, hair growth, and healing of injuries. Here’s a comprehensive look at PRP therapy:
What is PRP Therapy?
PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the concentrated platelets into the target area. Platelets are blood cells that play a crucial role in healing and tissue regeneration due to their growth factors and proteins.
The PRP Process
Blood Draw:
- A small amount of blood is drawn from the patient, typically from the arm.
Centrifugation:
- The blood is placed in a centrifuge, a machine that spins it at high speeds to separate its components. This process isolates the platelet-rich plasma from the red and white blood cells.
Preparation:
- The concentrated platelets are prepared for injection. This plasma is rich in growth factors that stimulate healing and tissue regeneration.
Injection:
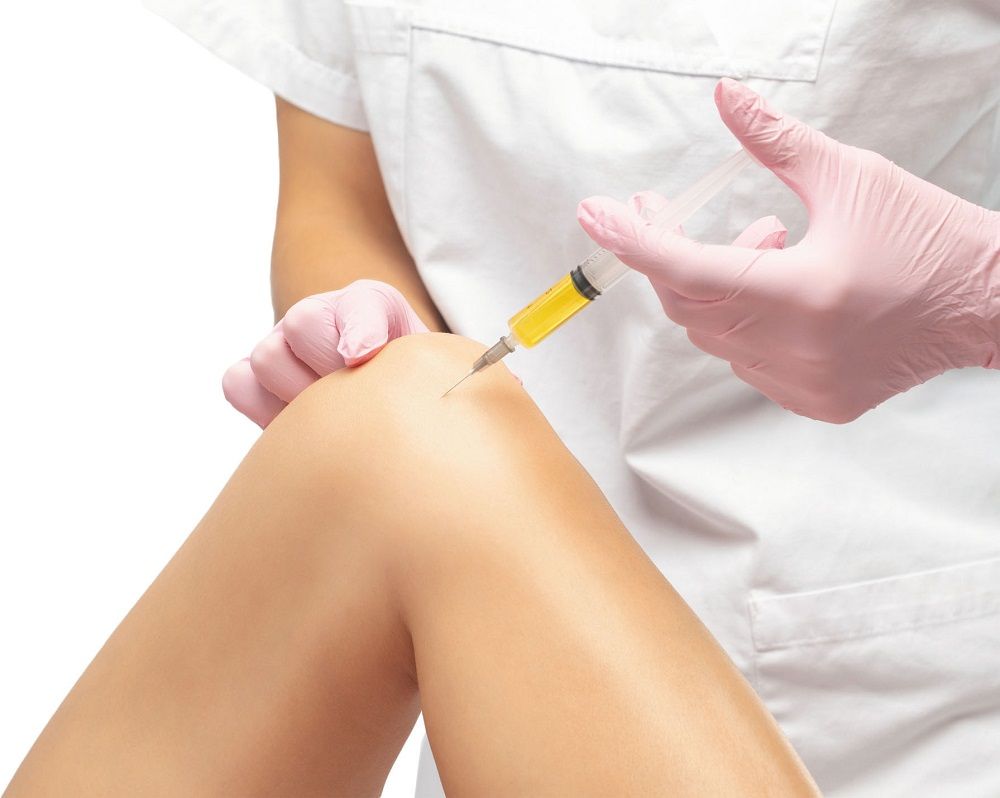
- The PRP is injected into the target area using a fine needle. The number of injections and treatment sessions may vary depending on the condition being treated.
Uses of PRP Therapy
Dermatology and Aesthetic Treatments:
- Skin Rejuvenation: PRP is used in facial rejuvenation treatments to improve skin texture, tone, and elasticity. It can reduce fine lines, wrinkles, and scars.
- Hair Restoration: PRP injections are used to stimulate hair growth in individuals with thinning hair or hair loss conditions such as androgenic alopecia.
Orthopedics and Sports Medicine:
- Joint Pain and Arthritis: PRP can be injected into joints to reduce pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
- Tendon and Ligament Injuries: It is used to promote healing in injuries like tennis elbow, Achilles tendinitis, and rotator cuff tears.
Wound Healing:
- PRP is used to enhance the healing of chronic wounds and ulcers, especially in diabetic patients.
Benefits of PRP Therapy
Natural and Autologous:
- PRP uses the patient’s own blood, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and infections.
Minimally Invasive:
- The procedure involves injections rather than surgery, resulting in minimal downtime and quick recovery.
Promotes Healing and Regeneration:
- Growth factors in PRP stimulate cell growth, tissue repair, and collagen production.
Versatile Applications:
- Effective in treating a wide range of conditions from skin aging to musculoskeletal injuries.
Risks and Considerations
Pain and Discomfort:
- Some patients may experience mild pain or discomfort at the injection site.
Infection:
- As with any injection, there is a small risk of infection, though this is minimized with proper sterile techniques.
Swelling and Bruising:
- Temporary swelling and bruising may occur at the injection site.
Individual Variability:
- Results can vary depending on individual health conditions and the area being treated.
Aftercare and Recovery
Rest:
- Patients are typically advised to rest the treated area for a short period after the procedure.
Avoid Strenuous Activity:
- Avoid heavy exercise or strenuous activity for a few days post-treatment to allow proper healing.
Follow-up:
- Follow-up appointments may be necessary to assess progress and determine if additional treatments are needed.
Conclusion
PRP therapy is a promising treatment that harnesses the body’s natural healing mechanisms to promote tissue regeneration and repair. It has a wide range of applications in dermatology, orthopedics, and aesthetic medicine, offering a natural and minimally invasive option for patients seeking rejuvenation and healing. Consulting with a qualified medical professional is essential to determine if PRP therapy is suitable for your specific condition and to ensure safe and effective treatment.



